The various types of cloud computing services have changed the game for anyone involved in information technology. Whether you’re an individual developer or a member of a larger IT department, you’ve probably already reaped some of the benefits.
We’re no longer worrying about resource demands because we can scale those instantly (and only pay for what we use). We don’t worry about storage capacities because those too can be increased immediately. Many times, we don’t even need to realize we have these needs because the cloud services figure it out for us and are flexible, expanding to fit our needs and simply billing us when the time comes.
[displayAd]
Types of Cloud Computing Services
The main benefits mentioned above have come through deployment, maintenance, and procurement. We’ve reaped these rewards through three models of cloud computing services.
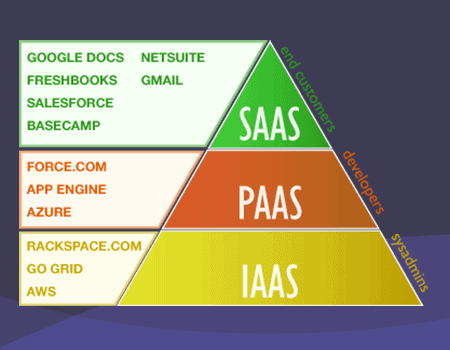
They are each explained below in expanding order, where each sequential service encompasses the previous:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
The first largely deals with the web architecture needed to host data and websites, whether on an intranet or the internet at large. These are the basic building blocks everyone needs but nobody wants to manage. The main needs of almost any business taking advantage of the web are:
- Storage
- Servers
- Networking
What makes these combined an “Infrastructure as a Service” is that they are managed and maintained by the company offering the service. The attributes of this cloud-based service that makes it desirable are the instant scaling of needs and the speed and redundancy of being distributed across many servers and hard drives. IaaS is typically used by sysadmins.
Among the companies offering IaaS are Amazon AWS, IBM Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle Cloud, and Rackspace. Our choices for the best cloud storage fall into the IaaS category, arguably, and the PaaS category below.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
An IT company using an IaaS will still need to manage the intricacies of deploying their software to the cloud and setting up the proper configurations. A PaaS takes care of that for you. Not only does it act as the infrastructure, but it behaves as a platform framework for your application to reside upon. This means that the service provider is taking care of the maintenance of the software that controls the infrastructure, patching the bugs, improving it, etc. Many from the web hosting world will know what I’m talking about if I mention WHM, cPanel, File Manager, and PHPmyAdmin.
What you can expect here is a reliable software architecture that controls the hardware and operating systems within the company’s cloud and integrates with the infrastructure flawlessly. All that’s left for you is to manage your own application, removing a huge technical burden from you and your staff. PaaS is typically used by developers.
Some examples of PaaS tech would be Mosso, Force, and the Google App Engine. Our best cloud hosting picks would all fall under the category of a PaaS.
[displayAd]
Software as a Service (SaaS)
This is (so far) the final evolutionary state of cloud computing services, the SaaS. In this case, you don’t even need to create an application to reside on a platform built on the cloud infrastructure. The software is already created for you as the end-user. In this case you will simply manage your data, leads, analytics, communications, and anything else the SaaS is capable of handling.
The challenge here, and it is a minor one, is finding the SaaS that is right for your company. But there are so many now, all geared towards specific businesses that you’ll have no troubles at all finding what you need. SaaS is typically used by end customers trying to avoid the need to code and develop their own solutions.
Some examples of SaaS technology that you’re likely familiar with are Google’s Gmail, Docs, and Sheets. Perhaps you’ve heard of Salesforce. Even things like Adobe Photoshop have become SaaS applications now.
Positive Consequences of the Cloud for Businesses
Previously, companies would have to hire an IT guy (or an entire department) who would meticulously set up a cluster computing network via LAN and even begrudgingly set up grid computing across several locations. Many small businesses were forced to learn this for themselves or to outsource the work to an outside agency, which creates all kinds of data security issues.
Now, with the cloud and the various types of cloud computing services, we can safely outsource our entire IT operations in a way that workers don’t even need to come to our premises. Not only is our data safe in terms of being replicated in case a server crashes, but it is safe in the security sense. You’d think workers at these cloud companies could access your data but it is all stored in an encrypted manner, safe from even their own prying eyes and those out malicious parties looking for software vulnerabilities. You can get various levels of privacy depending on the type of cloud deployment used.
Due to the economies of scale, everyone can take advantage of this computing revolution, from a mom looking to backup the photos from her kids sporting events, to small businesses needing a simple SaaS CRM software, all the way to multi-national billion-dollar companies. There is no barrier to entry thanks to the scaling costs.
[displayAd]
Conclusion
Depending on the sensitivity of your work, the style of cloud deployment you want (private, hybrid, or public), and the purpose for you using the cloud, you’ll find one of these three types of cloud computing services perfect for you. IaaS requires the most input but is most flexible. PaaS maintains a lot of the flexibility but removes some technical debt. And SaaS is likely what most of us want as individuals and smaller companies.
